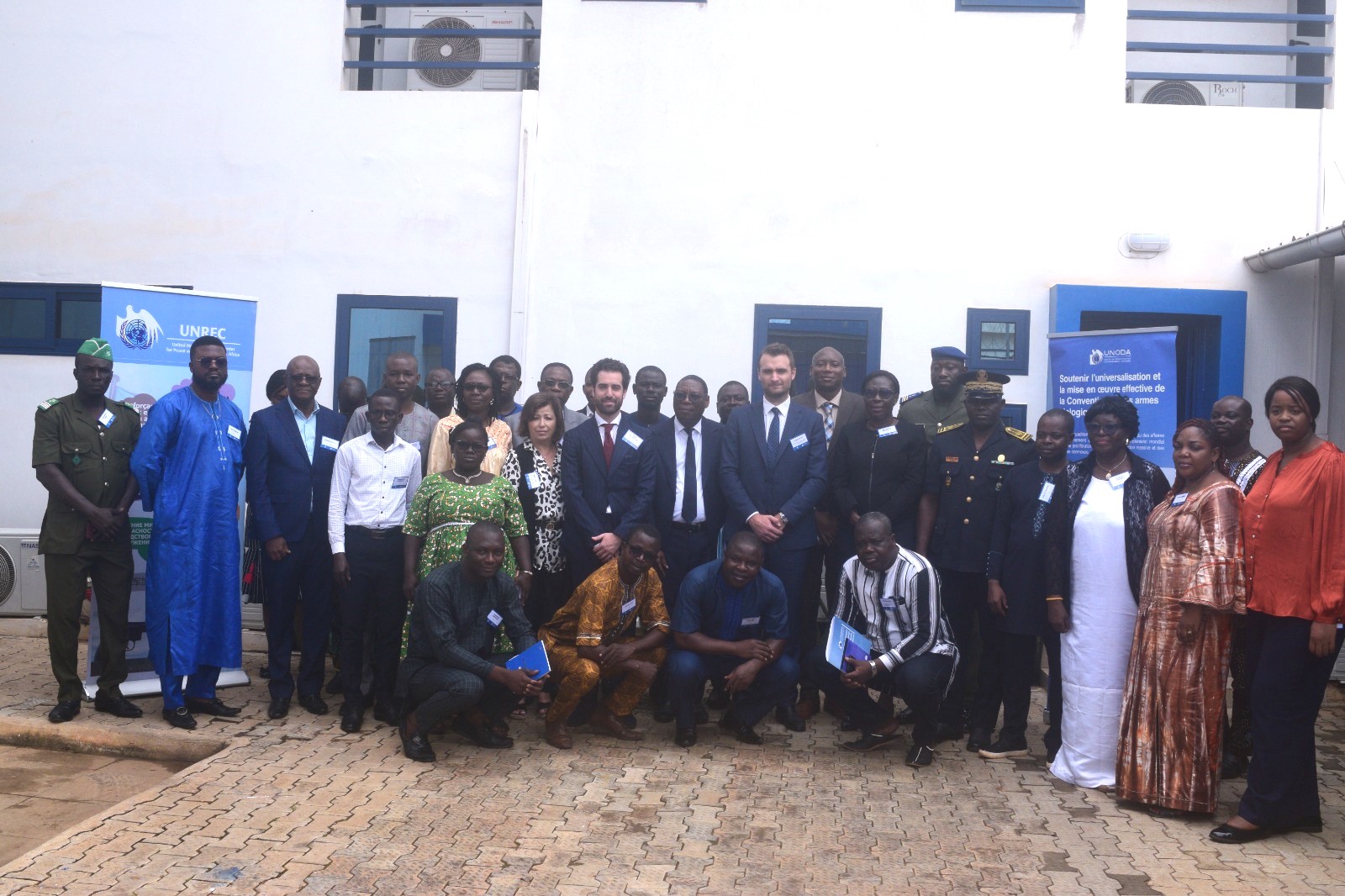
National workshop on strengthening the implementation of the BWC kickstart on 9 Oct. at UNREC premises.

As part of the project entitled "Supporting the universalization and effective implementation of the
Convention in Africa", the United Nations Office for Disarmament Affairs (UNODA) and its
Disarmament Affairs (UNODA) and its United Nations Regional Center for Peace and
Disarmament in Africa (UNREC) are organizing from October 9 to 10 at UNREC headquarters in Lomé (Togo)
a National Awareness Workshop on the Convention on the Prohibition of Biological and Toxin Weapons
and on the Preparation and Submission of Confidence-Building Measures in Togo.
The workshop, made possible with the financial support of France and the Global Partnership Against
proliferation of weapons of mass destruction and related materials, will bring together some 30 Togolese
representing over a dozen governmental and civil society stakeholders, as well as international
as well as international experts from Mali, the Kingdom of Morocco and UNODA.
The workshop provided an opportunity to exchange views on the importance and functioning of the Biological Weapons Convention, and to share best practices.
as well as the sharing of experience in its implementation at national level, in order to best support
Togolese efforts and priorities. Particular emphasis will be placed on
training on the preparation of Confidence Building Measures in Togo.
The aim of the event is to: (i) raise awareness of the importance and relevance of the
of the BWC; (ii) provide assistance
assistance in drafting BWC implementing legislation; (iii) support the preparation and submission of
and submission of confidence-building measures; and (iv) facilitate the creation or designation of national
contact points (NCPs).
The Biological Weapons Convention, adopted on April 10, 1972 and in force since
March 26, 1975, was the first multilateral disarmament treaty to ban an entire category of weapons
of mass destruction. With 185 States parties, the BWC established an unequivocal norm against biological
biological weapons, while facilitating assistance, international cooperation and capacity-building in fields
in areas such as biological science and technology, and preparedness and response to
and response to deliberate biological threats.

 Who we are
Who we are  What we do
What we do  Overview
Overview  Specific Projects
Specific Projects  Calendar of Events
Calendar of Events  Useful Links
Useful Links  Resolutions/SG Reports
Resolutions/SG Reports  Newsletter/UNREC Focus
Newsletter/UNREC Focus  Contact Us
Contact Us  Join Us
Join Us  Employment
Employment  Rosters of Experts
Rosters of Experts  Internships
Internships 
